
Stage-Gate Process | A Proven Approach for Successful Development
“Only 20% of the projects are progressing and reaching the planning stage in the UK; the rest failed” – says the latest news.
The dynamic world of innovation serves as the key foundation for product development and its structure. Sit back and imagine an ambitious startup that aims to launch a revolutionary project in which the team faces the daunting challenges of transforming their ideas into market-competitive products. Enter the stage gate process, a renowned crafted roadmap designed to direct the complexities of development methodologies.
Exploring it deeply reveals that this process is like a series that requires the team to meet the desired goals at every stage before moving on to the next. It is a journey of rigorous assessments and strategic decision-making that ensures every step is taken and leads toward success.
15 Second Summary!
What is the Stage-Gate Process? Concept and Methodology
The stage gate process has a rich history and remains a useful approach in industries where risk management and structured-based decisions are crucial. It is a project management technique that breaks the model into distinct stages with gates(decision points). The stage gate process bridges imagination and implementation, transforming bold ideas into successful stories.
Typically, the work is reviewed at every step to determine whether the project is able to move to the next stage. Moreover, this methodology is developed to prevent and minimize risk, allowing companies to work hard on more viable and profitable opportunities. Read the next sector to know why organizations should opt for this methodology whilst having a brief outlook on agile methodology – an incremental approach to software development.
Stage-Gate Vs. Agile Methodology – Which One is Better?
The debate on buzzing approaches is about which method companies should adopt. Can agile development methodologies enable the functionalities of the stage gate? Can stage gate offer a better framework for agile in a developing context? The answer is yes, both can work simultaneously; however, let’s get an overview of these approaches:
| Aspects | Agile Methods | Stage-Gate Process |
| Primary Focus | Micro projects | Macro projects |
| Project Phases | Sprint | Predefined |
| Planning Structure | Flexible | Rigid |
| Risk Assessment | Adaptive | Structured |
| Market Responsive | High | Potentially limited |
| Adaptability | Follows the plan | Adap the change |
However, every industry has different goals to achieve whilst adhering to timelines and regulatory standards. They can choose the best approach according to their requirements. Whilst agile is flexible and customer-collaborated, stage gate offers structured risk assessment and efficient resource allocation. Therefore, both ensure that every project step is adequately evaluated, producing a reliable framework to manage tasks and high-stakes projects.
Fundamental Principles and Objectives of Stage-Gate Process
The discovery-to-launch process is setting standards in the industry, standing out as one of the innovation management models that successfully incorporate all company directors into value-adding accountability. At its core, the stage gate procedure is developed on the following principles:
- Optimizes the innovative process completely
- Enhances in-company cross-functional teamwork
- Provides better returns on investments.
- Delivers better in-market success with new products and profitable sales.
- Takes option-based decisions
- Enhances collaboration with external development parties.
The Stages and Gates Explained
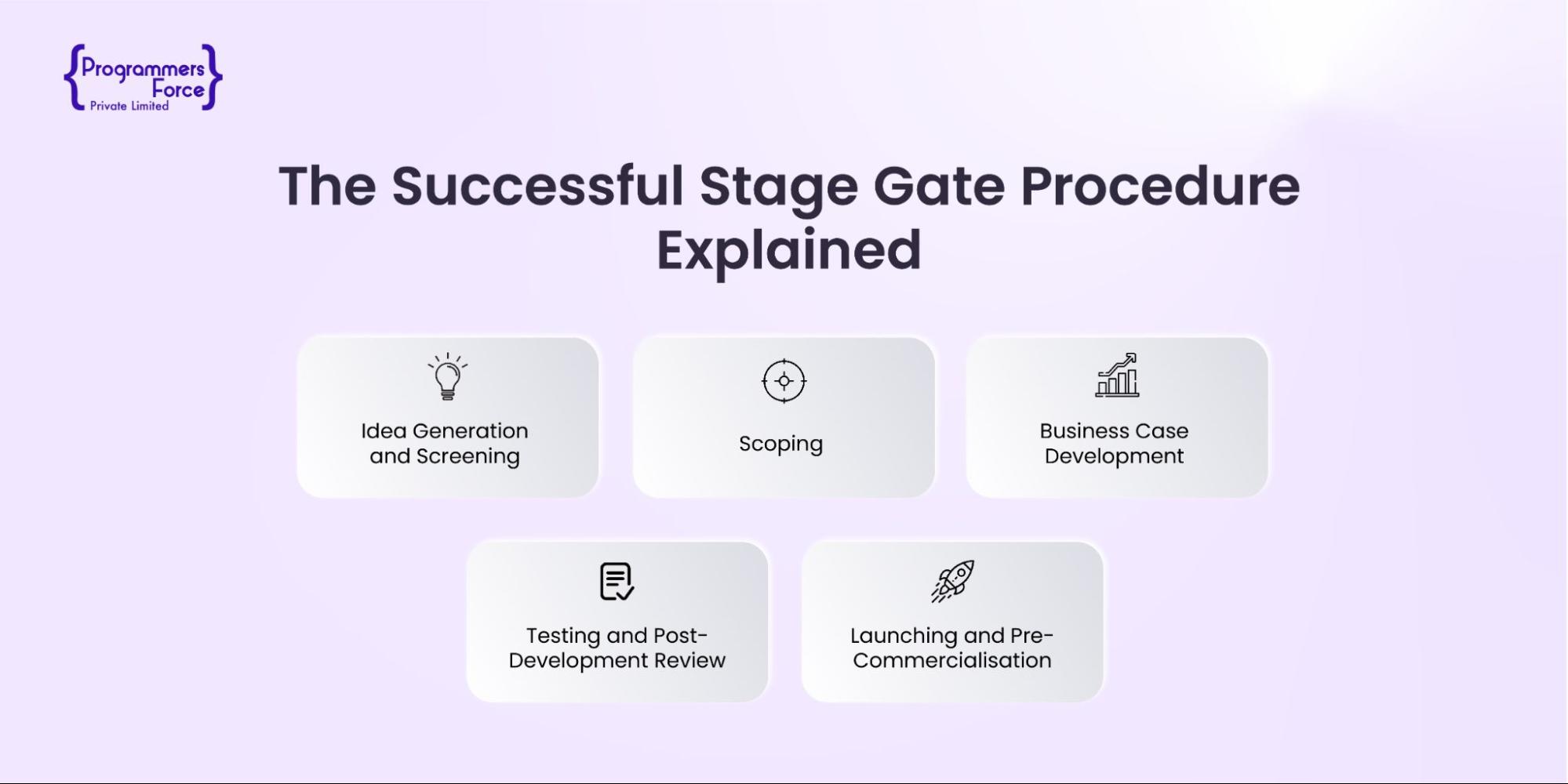
Every project has its own milestones; likewise, the stage gate process also represents some structures the company must pass to move the project model forward. Each stage plays a crucial role in launching a successful product whilst reducing the uncertainty factor from the development journey. Let’s explore the iterative process that is completed and followed by the gates:
Idea Generation and Screening
The primary goal of this step is to generate ideas for new products or enhance existing project models with the latest technologies and market trends. Brainstorm, research, and analyze the competition to outline potential ideas that align with business objectives. Once the idea comes into the spotlight, involve clients, teams, and stakeholders to pass the notion on for further work.
Scoping
Scoping in the stage gate process enables the development team to extensively understand and work through the plan. This stage helps the project with a technical assessment of financial implications and market aspects. An adequately analyzed project goal will result in estimating the resources and time required for the project development.
Business Case Development
This stage is responsible for developing a comprehensive business plan and the product, including extensive research and analysis of customer identification and potential profit estimation. Furthermore, it scrutinizes the entire process to ensure the goals are properly aligned with the nature of the business. As a result, proper prototypes and designs get a proper structure. The gate part in this approach decides whether to move the product and web development to testing and validation.
Testing and Post-Development Review
The developed models are sent for testing to ensure that the product meets all the requirements and is performing as expected in real-world complications. Gathering feedback from beta users to make necessary amendments is part of the post-development review, resulting in test reports and validation of product performance.
Launching and Pre-Commercialisation
To launch and advertise the product in the business market requires a successful plan and sales strategies with proper distribution channels. This phase focuses on marketing and pre-release commercialization. The final output received is a fully developed product ready for market deployment.
Implementation of Stage-Gate Process
| Strategies and Best Practices |
|
| Tools and Software |
|
| Customization |
|
Stage-Gate Process Proven Success Drivers
1. Go
The project is adequately developed! Launch it in the market because the tech world needs it. It’s time to hit the ground and execute the plan. Resources are allocated, and the team is ready to present the product.
2. Kill It
Sometimes, the ideas don’t work, maybe the industrial hurdles are unattainable, or there is a shift in the market trends. However, the efforts are not wasted but are relocated to other projects.
3. Hold On
The project may be kept on hold, but it can be just a temporary stop sign; the market could be evolving, or the project may need more information. Stay calm; the project can be revisited later under clear conditions and modifications.
4. Rework
The project is useful; however, it may need a little bit of amendments, user feedback, and additional work in order to meet the specific criteria. Refine the plan and present it again for evaluation.
5. Go With Condition
There is a high chance that the project can proceed further; still, a few uncertain conditions and amendments need to be made. Once the conditions are demonstrated, the model is taken further with external approvals secured.
Optimize Your Project Development With Programmer Force’s Stage Gate Methodology
Are you someone looking for a structured, efficient, and adaptive strategy that can help your product development procedure? Well! Here is what Programmer Force has to offer:
- Streamlined process
- Proper resource allocation
- Iterative feedbacks
- Customised solutions
- Benchmarks and much more.
You can benefit from leveraging the strategic approach of the stage gate process and ensuring a successful market launch in the tech world. Contact us or visit our website today to learn how PF can assist you in implementing a winning strategy.






